11. The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus (FTOC)
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus is the big aha! moment, and something you might have noticed all along:
- X-Ray and Time-Lapse vision let us see an existing pattern as an accumulated sequence of changes
- The two viewpoints are opposites: X-Rays break things apart, Time-Lapses put them together
This might seem "obvious", but it's only because we've explored several examples. Is it truly obvious that we can separate a circle into rings to find the area? The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus gently reminds us we have a few ways to look at a pattern. ("Might I suggest the ring-by-ring viewpoint? Makes things easier to measure, I think.")
Part 1: Shortcuts For Definite Integrals
If derivatives and integrals are opposites, we can "shortcut" the manual accumulation process involved in definite integrals.
For example, what is 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9? (Let's accumulate discrete steps because they're simpler to visualize.)
The hard way, using the definite integral, is to start cranking through the addition. The easy way is to realize that pattern came from a growing square. We know the last change (+9) happened at x=4, so we've built up to a 5×5 square. Therefore, the sum of the entire sequence is 25:
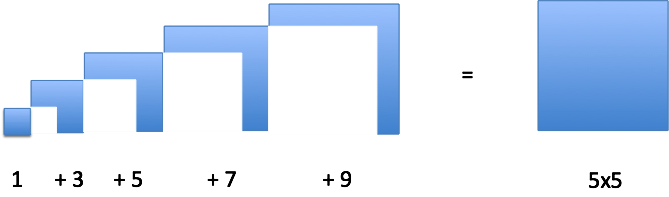
Neat! If we have the original pattern, we have a shortcut to measure the size of the steps.
How about a partial sequence like 5 + 7 + 9? Well, just take the total accumulation and subtract the part we're missing (in this case, the missing 1 + 3 represents a missing 2×2 square).
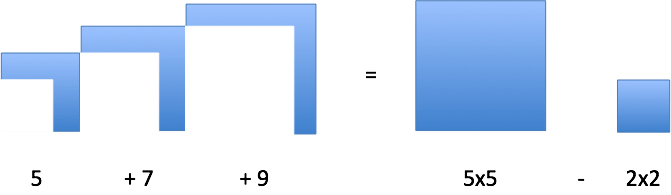
And yep, the sum of the partial sequence is: 5×5 - 2×2 = 25 - 4 = 21.
I hope the strategy clicks for you: we avoid manually computing the definite integral by finding the original pattern.
Here's the first part of the FTOC in fancy language. If we have pattern of steps and the original pattern, the shortcut for the definite integral is:
$$ \int_a^b steps(x) dx = Original(b) - Original(a)$$
Intuitively, I read this as "Adding up all the changes from a to b is the same as getting the difference between a and b". Formally, you'll see $$$f(x) = steps(x)$$$ and $$$F(x) = Original(x)$$$, which I think is confusing. Label the steps as steps, and the original as the original.
Why is this cool? The definite integral is a gritty mechanical computation, and the indefinite integral is a nice, clean formula. Just take the difference between the endpoints to know the net result of what happened in the middle! (That makes sense, right?)
Part 2: Finding The Indefinite Integral
Ok. Part 1 said that if we have the original function, we can skip the manual computation of the steps. But how do we find the original?
FTOC Part Deux to the rescue!
Let's pretend there's some original function (currently unknown) that tracks the accumulation:
$$ Accumulation(x) = \int_a^b steps(x) dx$$
The FTOC says the derivative of that magic function will be the steps we have:
$$ Accumulation'(x) = steps(x) $$
Now we can work backwards. If we can find some random function, take its derivative, notice that it matches the steps we have, we can use that function as our original!
Skip the painful process of thinking about what function could make the steps we have. Just take a bunch of them, break them, and see which matches up. It's our vase analogy, remember? The FTOC gives us "official permission" to work backwards. In my head, I think "The next step in the total accumuation is our current amount! That's why the derivative of the accumulation matches the steps we have."
Technically, a function whose derivative is equal to the current steps is called an anti-derivative (One anti-derivative of 2 is 2x; another is 2x + 10). The FTOC tells us any anti-derivative will be the original pattern (+C of course).
This is surprising -- it's like saying everyone who behaves like Bill Cosby is Bill Cosby. But in calculus, if a function has steps that match the ones we're looking at, it's the original source.
The practical conclusion is integration and differentiation are opposites. Have a pattern of steps? Integrate to get the original. Have the original? Differentiate to get the pattern of steps. Jump back and forth as many times as you like.
Next Steps
Phew! This was a theory-heavy set of lessons. It was hopefully enough to make the connections click. I'm most interested in developer metaphorical understanding, and leave the detailed proofs to a follow-up. No need to recite the recipe before tasting the meal.
The key insights from:
- Infinity: A finite result can be viewed with a sequence of infinite steps
- Derivatives: We can take a knowingly-flawed measurement and morph it into the ideal one
- Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus: We can use the original function as a shortcut to track the intermediate steps
In the upcoming lessons, we'll work through a few famous calculus rules and applications. The ultimate goal will be to work out, for ourselves, how to make this happen:
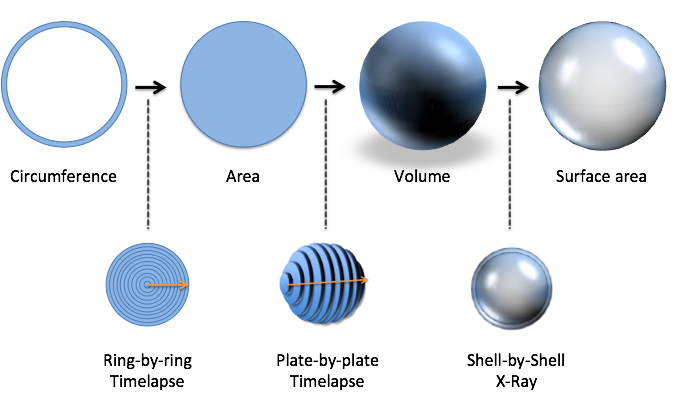
We have an intuitive understanding the sequence above is possible. By the end, you'll be able to play the music on your own.