Once you understand flux intuitively, you don’t need to memorize equations. The formulas become “obvious” dare I say. However, it took a lot of effort to truly understand that:
- Flux is the amount of “something” (electric field, bananas, whatever you want) passing through a surface.
- The total flux depends on strength of the field, the size of the surface it passes through, and their orientation.
Your vector calculus math life will be so much better once you understand flux. And who doesn’t want that?
Physical Intuition
Think of flux as the amount of something crossing a surface. This “something” can be water, wind, electric field, bananas, pretty much anything you can imagine. Math books will use abstract concepts like electric fields, which is pretty hard to visualize. I find bananas more memorable, so we’ll be using those.
To measure the flux (i.e. bananas) passing through a surface, we need to know
- The surface you are considering (shape, size and orientation)
- The source of the flux (strength of the field, and which way it is spitting out
bananasflux)
The strength of the field is important – would you rather have a handful of \$5 or \$20 bills “flux” into your bank account? Would you rather have a big or little banana come your way? No need to answer that one.
Background Ideas
Keep a few ideas in mind when considering flux:
Vector Field: This is the source of the flux: the thing shooting out bananas, or exerting some force (like gravity or electromagnetism). Flux doesn’t have to be a physical object — you can measure the “pulling force” exerted by a field.
Surface: This is the boundary the flux is crossing through or acting on. The boundary could be a sphere, a plane, even the top of a bucket. Notice that the boundary may not exist — the top of a bucket traces out a circle, but the hole isn’t actually there. We’re considering the flux passing through the region the circle defines.
Timing: We measure flux at a single point in time. Freeze time and ask “Right now, at this moment, how much stuff is passing through my surface?”. If your field doesn’t change over time, then all is well. If your field does change, then you need to pick a point in time to measure the flux.
Measurement: Flux is a total, and is not “per unit area” or “per unit volume”. Flux is the total force you feel, the total number of bananas you see flying by your surface. Think of flux like weight. (There is a separate idea of "flux density" (flux/volume) called divergence, but that’s a separate article.)
Flux Factors
The source of flux has a huge impact on the total flux. Doubling the source (doubling the “banana-ness” of each banana), will double the flux passing through a surface.
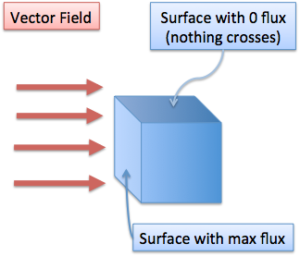
Total flux also depends on the orientation of the field and the surface. When our surface completely faces the field it captures maximum flux, like a sail facing directly into the wind. As the surface tilts away from the field, the flux decreases as less and less flux crosses the surface.
Eventually, we get zero flux when the source and boundary are parallel — the flux is passing over the boundary, but not crossing through it. It would be like holding a bucket sideways under a waterfall. You wouldn’t capture much water (ignoring splashing) and may get a few funny looks.
Total flux also depends on the size of our surface. In the same field, a bigger bucket will capture more flux than a smaller one. When we figure out our total flux, we need to see how much field is passing through our entire surface.
This is simple stuff so far, right? If you forget, just think about capturing water from a waterfall. What matters? The strength of the waterfall, the size of the bucket and the orientation of the bucket.
Positive and Negative Flux
One last detail – we need to decide on a positive and negative direction for flux. This decision is arbitrary, but by convention (aka your math teacher will penalize you if you don’t agree), positive flux leaves a closed surface, and negative flux enters a closed surface.
Think of flux as a hose spraying water. Positive flux means flux is leaving the hose; the hose is a source of flux. Negative flux is like water entering a sink; it is a sink of flux. So positive flux = leaving, negative = entering. Got it? (By the way, the terms “source” and “sink” are sometimes used to describe fields).
Quick Summary
Quick checkpoint: Flux depends on
- The size of the surface
- Magnitude of the source field
- The angle between them
A fire hose shooting at a tiny bucket (small surface, large magnitude) could have the same flux as a garden hose aimed at a large bucket (large surface, small magnitude). And in case you forgot, flux reminds us to hold the bucket so it is facing the source. This should be obvious – but don’t you want ideas (especially in math!) to be obvious?
Math Intuition
Now that we have a physical intuition, let’s try to derive the math. In most cases, the source of flux will be described as a vector field: Given a point (x,y,z), there's a formula giving the flux vector at that point.
We want to know how much of that vector field is acting/passing through our surface, taking the magnitude, orientation, and size into account. From our intuition, it should look something like this:
Total flux = Field Strength * Surface Size * Surface Orientation
However, this formula only works if the vector field is the same at every point. Usually, it’s not, so we’ll take the standard calculus approach to solving problems:
- Divide the surface into pieces
- Find the flux at each piece
- Add up the small units of flux to get total flux (integrate).
Let’s go out on a limb and call the tiny piece of the surface dS. Total flux is:
Total flux = (Field Strength * dS * Orientation) for every dS.
or
Total flux = Integral (Field Strength * Orientation * dS)
Make sense so far? Now, we need to figure out how much orientation actually matters. Like we said before, if the field and the surface are parallel, then there is zero flux. If they are perpendicular, there is full flux.
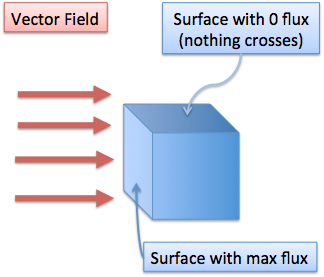
(In this diagram, the flux is parallel with the top surface, and nothing enters from that direction. Mathematically, we represent surfaces by their normal vector, which sticks out of the surface. Don’t let this bookkeeping detail disrupt your visualization.)
If there is an angle, then it is some factor in-between:
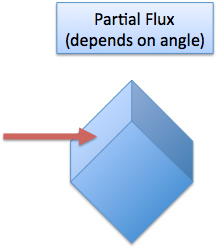
How much, exactly? Well, this is a job for the dot product, which is the projection of the field onto the surface. The dot product gives us a number (from 0 to 1) that tells us what percent of the field is passing through the surface. So, the equation becomes:
Total flux = Integral( Vector Field Strength dot dS )
And finally, we convert to the stuffy equation you’ll see in your textbook, where F is our field, S is a unit of area and n is the normal vector of the surface:
![]()
Time for one last detail — how do we find the normal vector for our surface?
Good question. For a surface like a plane, the normal vector is the same in every direction. For a sphere, the normal vector is in the same direction as $\vec{r}$, your position on the sphere: the top of a sphere has a normal vector that goes out the top; the bottom has one going out the bottom, etc.
More complicated shapes may have a normal vector that varies quite a bit. In this case, try to break the shape into smaller regions (like spheres, cylinders and planes) and find the flux in each part. Then, add up the flux in each region to get the total flux (keeping in mind positive and negative flux).
If the shape is more complicated than that, you may need a computer model or more advanced theorems; but at least you know what is happening behind the scenes.
Flux Examples
Let’s do a few thought experiments to understand flux. Imagine a tube, that lets water pass right through it. We hold the tube under a waterfall, wait a few seconds, then ask what the flux is. I want a numeric answer – what is the flux?
You might think we need to know the speed of the waterfall, the size of the tube, the orientation, etc. But that isn’t the case.
Remember our convention for flux orientation: positive means flux is leaving, negative means flux is entering. In this example, water is falling downward, or entering the tube. This means the top surface has negative flux (it appears to be siphoning up water).
However, what’s happening at the bottom of the box? The water passed through the top and is now leaving the bottom, which is positive flux:
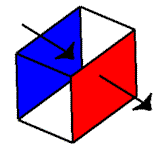
Ah, this beautiful diagram shows what is going on. The top of the box / tube says that water is entering, and the bottom says water is leaving. Assuming the same amount of water is leaving and entering (the rate of water falling is a constant), the net flux would be zero. Think of it as X + (-X) = 0.
What if we had increased the rate of water? Decreased? What would happen?
My (possibly incorrect) answer: If we increased the rate, it means more water would enter than leaves, for a brief moment. We’d have a momentary spike in negative flux (the tube would look like a sink), until the rates equalized. Vice versa if we decreased the rate of water – we’d have a brief spike of positive flux (more water was leaving than entering), until the rate equalized.
Even though net flux is zero, this is different from having zero flux pass through each surface. If you are in an empty field, no shape will generate any flux. But if you are in a field where flux is canceling, changing your shape or orientation could create a non-zero flux. Recognize the difference between having zero flux because the field is zero, vs. having all the flux cancel.
One more point – the “tube” we are considering is a region we define, not a physical tube. Measuring flux is about drawing imaginary boundaries, not having a physical shape. So, when we define the region of a “bucket”, it would not “fill up” with flux. Flux is what is passing through the sides of a bucket at a moment in time. Clearly, if we put in a physical bucket it would fill up, but that’s not what we’re measuring. We’re seeing how much flux would be entering a region we define, from any and all sides (not just the opening). Got it?
And one more point. We haven’t really talked about the units of flux. What is it measured in? As far as I understand, the units can be anything – it depends on the unit of your vector field. So, your vector field might represent bananas, in which case you get total bananas crossing a surface. Or, your field could represent bananas-per-second, in which case you’d get the bananas-per-second crossing your surface. The units of flux depend on the units of your vector field.
Flux is relatively simple to understand, and is really helpful in vector calculus and physics. Trying to understand flux by looking at a mess of integrals is not the way to go. First get an intuitive understanding, and the details will make more sense.
Insights
Here’s a few insights that hit me after learning about flux:
You can take the time derivative of flux. If the vector field (F) changes with time (t), you can use dF/dt to see how the total flux changes over time. Even though flux is taken at a unit in time, you can measure flux at two consecutive moments to see how fast it is changing.
You can integrate flux, which means finding how much flux has crossed over a certain time. If the field F is constant over time, you can multiply the flux at one instant by your duration. But if F changes with time, then you need to measure at each moment and integrate. Each flux calculation is done at an instant of time, then they are summed together. Again, this is the standard calculus technique.
In our waterfall example, we looked at a single point in time where water had been flowing for a while. If we chose an early point in time, we would have negative flux: water had entered the top, but not yet left the bottom. If we turned off the water, there’d be an instant in time with positive flux: water had stopped entering, but was continuing to leave.
Flux is important for math, electricity and magnetism, and your science life will be better for knowing it. Your social life – not so much.
This was a long article. Take a break. Take a shower. Get outside. See your family. Or, read on about divergence. It’s your call.
Other Posts In This Series
- Vector Calculus: Understanding the Dot Product
- Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
- Vector Calculus: Understanding Flux
- Vector Calculus: Understanding Divergence
- Vector Calculus: Understanding Circulation and Curl
- Vector Calculus: Understanding the Gradient
- Understanding Pythagorean Distance and the Gradient